Search
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- Search
- Article
- Exploring Factors Influencing Attitudes towards COVID-19 Prevention Measures and Compliance with Behavioral Guidelines
- Savannah Kelly, Hyoungkoo Khang
- Received November 21, 2023 Accepted April 22, 2024 Published online April 24, 2024
-
[Epub ahead of print]
-
 Full text
Full text  PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub  PDF
PDF

- Original Articles
- Trust in social media is associated with misperceptions about COVID-19
- Jagadish Thaker, Somrita Ganchoudhuri
- Health New Media Res. 2023;7(1):1-13. Published online June 30, 2023
-
 Full text
Full text  PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub  PDF
PDF

- A discourse appraisal of conspiracy perceptions about COVID-19 and its vaccine in Nigeria’s social media space
- Emmanuel Chinaguh, Kehinde Adeosun, Hannah Adejumobi
- Health New Media Res. 2022;6(2):213-226. Published online December 31, 2022
-
 Full text
Full text  PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub  PDF
PDF
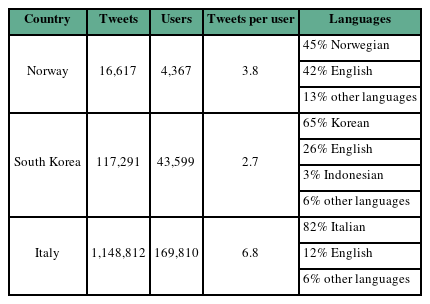
- Global health, global networks: a multilingual network approach to COVID-19 tweets in Norway, Korea, and Italy
- Jessica Yarin Robinson
- Health New Media Res. 2022;6(2):174-188. Published online December 31, 2022
-
 Full text
Full text  PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub  PDF
PDF
- Fake news and misinformation on COVID-19: implications for media credibility in Nigeria
- Desmond Onyemechi Okocha, Samuel Matthew Akpe
- Health New Media Res. 2022;6(1):139-161. Published online June 30, 2022
-
 Full text
Full text  PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub  PDF
PDF
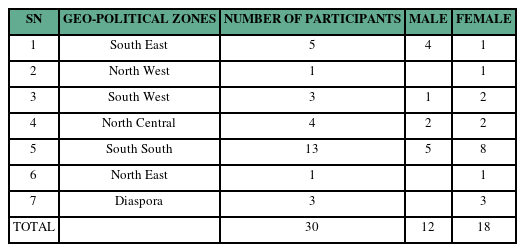
- Knowledge, perception and response to new media messages on COVID-19 among residents of a rural community in Nigeria
- Tsegyu Santas, Kelvin Inobemhe, Nick-Tansi Saint Udeh
- Health New Media Res. 2022;6(1):103-138. Published online June 30, 2022
-
 Full text
Full text  PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub  PDF
PDF
- “The mask is not for you”: a framing analysis of pro- and anti-mask sentiment on Twitter
- Scott S.D. Mitchell, Josh Beanlands
- Health New Media Res. 2022;6(1):3-34. Published online June 30, 2022
-
 Full text
Full text  PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub  PDF
PDF

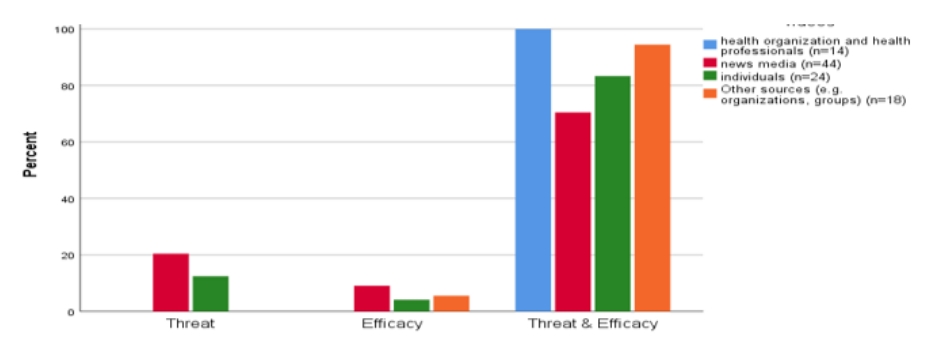
- YouTube as a source of health information: an analysis of videos on COVID-19
- Jamal Uddin, Mohammad Aminul Islam
- Health New Media Res. 2021;5(2):251-277. Published online December 31, 2021
-
 Full text
Full text  PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub  PDF
PDF
- Assessing the use of the WhatsApp status updates tool for COVID-19 relevant health communication among undergraduate communication students in Ghana
- Emmanuel Essel
- Health New Media Res. 2021;5(1):91-120. Published online June 30, 2021
-
 Full text
Full text  PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub  PDF
PDF

-
Health &
New Media
ResearchPrint ISSN: 2671-4124
Online ISSN: 2951-2522












